Synuclein-α Monoclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YM0606
- Applications:WB;IHC;IF;ELISA
- Reactivity:Human
- Target:
- Synuclein-α
- Fields:
- >>Alzheimer disease;>>Parkinson disease;>>Pathways of neurodegeneration - multiple diseases
- Gene Name:
- SNCA
- Protein Name:
- Alpha-synuclein
- Human Gene Id:
- 6622
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P37840
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- O55042
- Immunogen:
- Purified recombinant fragment of Synuclein-α expressed in E. Coli.
- Specificity:
- Synuclein-α Monoclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Synuclein-α protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Monoclonal, Mouse
- Dilution:
- WB 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC 1:200 - 1:1000. ELISA: 1:10000.. IF 1:50-200
- Purification:
- Affinity purification
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- SNCA;NACP;PARK1;Alpha-synuclein;Non-A beta component of AD amyloid;Non-A4 component of amyloid precursor;NACP
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 14kD
- References:
- 1. J. Johnson, S. M. Hague, M. Hanson. Neurology, Aug 2004; 63: 554 – 556
2. Hong Tao Li, Xiao Jing Lin, Yuan Yuan Xie. Protein Pept Lett. 2006;13(4):385-90.
- Background:
- Alpha-synuclein is a member of the synuclein family, which also includes beta- and gamma-synuclein. Synucleins are abundantly expressed in the brain and alpha- and beta-synuclein inhibit phospholipase D2 selectively. SNCA may serve to integrate presynaptic signaling and membrane trafficking. Defects in SNCA have been implicated in the pathogenesis of Parkinson disease. SNCA peptides are a major component of amyloid plaques in the brains of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Alternatively spliced transcripts encoding different isoforms have been identified for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2016],
- Function:
- alternative products:Additional isoforms seem to exist,disease:Brain iron accumulation type 1 (NBIA1, also called Hallervorden-Spatz syndrome), a rare neuroaxonal dystrophy, is histologically characterized by axonal spheroids, iron deposition, Lewy body (LB)-like intraneuronal inclusions, glial inclusions and neurofibrillary tangles. SNCA is found in LB-like inclusions, glial inclusions and spheroids.,disease:Defects in SNCA are a cause of autosomal dominant Parkinson disease 1 (PARK1) [MIM:168601, 168600]. Parkinson disease (PD) is a complex, multifactorial disorder that typically manifests after the age of 50 years, although early-onset cases (before 50 years) are known. PD generally arises as a sporadic condition but is occasionally inherited as a simple mendelian trait. Although sporadic and familial PD are very similar, inherited forms of the disease usually begin at earlier ages an
- Subcellular Location:
- Cytoplasm . Membrane . Nucleus . Cell junction, synapse . Secreted . Cell projection, axon . Membrane-bound in dopaminergic neurons (PubMed:15282274). Expressed and colocalized with SEPTIN4 in dopaminergic axon terminals, especially at the varicosities (By similarity). .
- Expression:
- Highly expressed in presynaptic terminals in the central nervous system. Expressed principally in brain.
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images

- Western Blot analysis using Synuclein-α Monoclonal Antibody against truncated Synuclein-α recombinant protein.
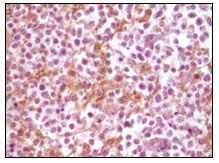
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human glioma tissue, showing membrane localization with DAB staining using Synuclein-α Monoclonal Antibody.
