PPAR-γ Monoclonal Antibody
- Catalog No.:YM1082
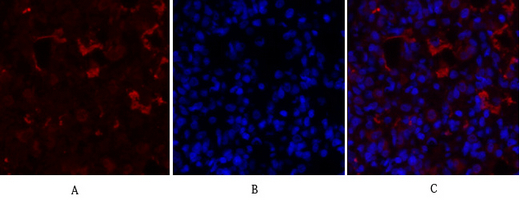
- Applications:WB;IF
- Reactivity:Human;Mouse;Rat;Bovine;Dog;Goat;Pig;Rabbit;sheep
- Target:
- PPAR-γ
- Fields:
- >>PPAR signaling pathway;>>AMPK signaling pathway;>>Longevity regulating pathway;>>Osteoclast differentiation;>>Thermogenesis;>>Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease;>>Huntington disease;>>Pathways in cancer;>>Transcriptional misregulation in cancer;>>Thyroid cancer;>>Lipid and atherosclerosis
- Gene Name:
- PPARG
- Protein Name:
- Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma
- Human Gene Id:
- 5468
- Human Swiss Prot No:
- P37231
- Mouse Gene Id:
- 19016
- Mouse Swiss Prot No:
- P37238
- Rat Gene Id:
- 25664
- Rat Swiss Prot No:
- O88275
- Immunogen:
- Purified recombinant human PPAR-γ (C-terminus) protein fragments expressed in E.coli.
- Specificity:
- PPAR-γ Monoclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of PPAR-γ protein.
- Formulation:
- Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
- Source:
- Monoclonal, Mouse
- Dilution:
- WB 1:1000 - 1:2000. IF 1:100 - 1:500. Not yet tested in other applications.
- Purification:
- Affinity purification
- Concentration:
- 1 mg/ml
- Storage Stability:
- -15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
- Other Name:
- PPARG;NR1C3;Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma;PPAR-gamma;Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group C member 3
- Molecular Weight(Da):
- 58kD
- Background:
- peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma(PPARG) Homo sapiens This gene encodes a member of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) subfamily of nuclear receptors. PPARs form heterodimers with retinoid X receptors (RXRs) and these heterodimers regulate transcription of various genes. Three subtypes of PPARs are known: PPAR-alpha, PPAR-delta, and PPAR-gamma. The protein encoded by this gene is PPAR-gamma and is a regulator of adipocyte differentiation. Additionally, PPAR-gamma has been implicated in the pathology of numerous diseases including obesity, diabetes, atherosclerosis and cancer. Alternatively spliced transcript variants that encode different isoforms have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
- Function:
- alternative products:Additional isoforms seem to exist,disease:Defects in PPARG are the cause of familial partial lipodystrophy type 3 (FPLD3) [MIM:604367]. Familial partial lipodystrophies (FPLD) are a heterogeneous group of genetic disorders characterized by marked loss of subcutaneous (sc) fat from the extremities. Affected individuals show an increased preponderance of insulin resistance, diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia.,disease:Defects in PPARG can lead to type 2 insulin-resistant diabetes and hyptertension.,disease:Defects in PPARG may be associated with colon cancer.,disease:Defects in PPARG may be associated with susceptibility to obesity [MIM:601665].,disease:Variation in PPARG is associated with carotid intimal medial thickness 1 (CIMT1) [MIM:609338]. CIMT is a measure of atherosclerosis that is independently associated with traditional atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
- Subcellular Location:
- Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Redistributed from the nucleus to the cytosol through a MAP2K1/MEK1-dependent manner. NOCT enhances its nuclear translocation.
- Expression:
- Highest expression in adipose tissue. Lower in skeletal muscle, spleen, heart and liver. Also detectable in placenta, lung and ovary.
魏孔熙, et al. "黄芪多糖对 X 线辐射骨髓间充质干细胞成脂分化的影响." Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University (Medical Sciences) 41.2 (2020).
- June 19-2018
- WESTERN IMMUNOBLOTTING PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY-PARAFFIN PROTOCOL
- June 19-2018
- IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE PROTOCOL
- September 08-2020
- FLOW-CYTOMEYRT-PROTOCOL
- May 20-2022
- Cell-Based ELISA│解您多样本WB检测之困扰
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-ACETYL-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- CELL-BASED-ELISA-PROTOCOL-FOR-PHOSPHO-PROTEIN
- July 13-2018
- Antibody-FAQs
- Products Images
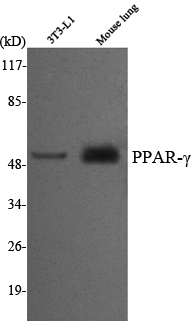
- Western Blot analysis using PPAR-γ Monoclonal Antibody against 3T3-L1, mouse lung cell lysate.